SHA-1
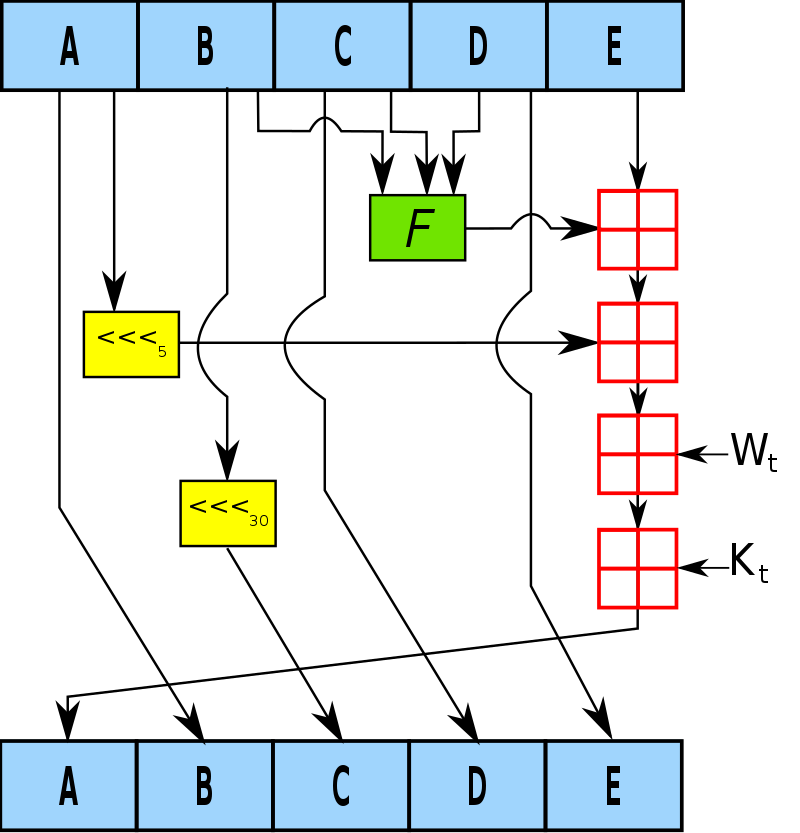
What is SHA-1
The goal of this project was to produce an implementation of the deprecated SHA-1 (Secure Hash Algorithm 1) cryptographic hash function in C that was able to take in and encrypt text files. SHA-1, developed by the National Security Agency (NSA), was a widely adopted cryptographic hash function that was designed to take an input (or “message”) and produce a fixed-size output, commonly referred to as a “hash.” It was widely utilized in various security protocols and applications, such as digital signatures, software protection, and file integrity verification. However, due to recent advancements in the field of cryptography and the discovery of collision vulnerabilities, its usage has been officially deprecated by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in 2011. Despite being considered as a broken hash function, this project aimed to demonstrate the inner workings of the algorithm and its usage for educational and research purposes.
Responsibilities and Lessons
As this was an individual project, the entirety of the code was written on my own. This project was a valuable learning experience that taught me several lessons about cryptographic hash functions and their implementation in code. Specifically, it highlighted the importance of understanding the underlying mathematical concepts of a cryptographic algorithm. The process of writing an implementation of SHA-1 required a thorough understanding of the algorithm, including the various logical operations and bitwise rotations that it is based on. This was essential in order to properly implement the algorithm in code, and it required a great deal of attention to detail in order to ensure the accuracy of the final product. Overall, writing an implementation of SHA-1 in C was a challenging but rewarding experience.
Sample Code
Here is some code of a helper function that assists in performing bit-wise operations:
unsigned int f(unsigned int t, unsigned int B, unsigned C, unsigned D){
unsigned int output = 0;
if ((0 <= t) && (t <= 19)){
output = (B & C) | ((~B) & D);
}
else if ((20 <= t) && (t <= 39)){
output = (B ^ C ^ D);
}
else if ((40 <= t) && (t <= 59)){
output = (B & C) | (B & D) | (C & D);
}
else if ((60 <= t) && (t <= 79)){
output = (B ^ C ^ D);
}
return output;
}
Source : GitHub.